Can Dogs Eat Marshmallows? 7 Safety Guidelines + Risks
Quick Answer: Can Dogs Eat Marshmallows?
Can dogs eat marshmallows? No, dogs should not eat marshmallows. Here’s why:
- Regular marshmallows: High sugar content causes obesity, dental problems, and choking risks
- Sugar-free marshmallows: Contain xylitol which is toxic and potentially fatal to dogs
- Chocolate marshmallows: Contain chocolate which is poisonous to dogs
Safe alternatives: Apple slices, carrots, plain rice cakes, or dog-specific treats.
Emergency: If your dog ate sugar-free or chocolate marshmallows, contact your vet immediately.
As a dog owner, you’ve probably asked yourself, “Can dogs eat marshmallows?” when your furry friend gives you those pleading eyes during a campfire s’mores session or while you’re enjoying hot chocolate with these fluffy treats. The short answer requires careful consideration of several factors affecting your pet’s health and safety.
This comprehensive guide explores whether marshmallows are safe for dogs, the potential risks they pose, and provides seven essential guidelines every responsible pet owner should follow when it comes to these sweet treats.
Table of Contents
Are Marshmallows Safe for Dogs? (3-Second Safety Check)
Many dog owners wonder, “Can dogs eat marshmallows safely?” The answer depends on the type:
- Contains xylitol? → NEVER give to dogs (call vet if consumed)
- Does it have a chocolate coating? → NEVER give to dogs (toxic)
- Regular marshmallow? → Avoid (choking risk + unnecessary sugar)
Bottom line: When asking “Can dogs eat marshmallows?” the safest answer is always no.
Understanding Marshmallows: Composition and Ingredients
Before determining whether dogs can have marshmallows, it’s important to understand what these puffy confections actually contain.
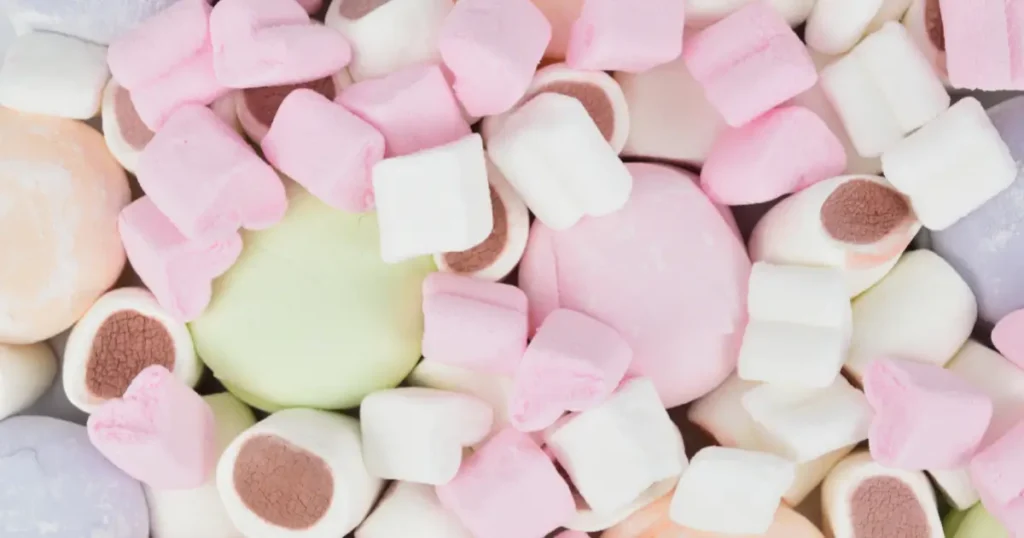

Standard Marshmallow Ingredients
Most commercial marshmallows contain:
- Sugar (often as the primary ingredient)
- Corn syrup or high fructose corn syrup
- Gelatin (typically derived from animal collagen)
- Modified corn starch
- Water
- Flavorings (vanilla or other artificial flavors)
- Artificial colors
- Sometimes egg whites or whipped egg protein
- Occasionally preservatives
In specialty or gourmet marshmallows, you might also find:
- Honey or other natural sweeteners
- Fruit juices or purees
- Natural colors from vegetable sources
- Additional flavorings
- Chocolate coatings
- Nuts or other mix-ins
Understanding these ingredients is essential when determining are marshmallows bad for dogs because several components raise concerns for canine consumption.
Types of Marshmallows
Different marshmallow varieties present different levels of concern when considering can dogs eat marshmallows:
- Normal marshmallows: Generally free of immediate toxins, but high in sugar
- Mini marshmallows: Present a potentially higher choking risk for small dogs
- Sugar-free marshmallows: could contain xylitol, a substance that is highly toxic to dogs.
- Flavored varieties: Often contain additional artificial ingredients
- Chocolate-covered marshmallows: Contain chocolate, which is toxic to dogs
- Marshmallow fluff/cream: Contains similar sugar concerns, but in a different form
With this understanding of marshmallow composition, let’s explore seven essential safety guidelines to follow.
7 Essential Safety Guidelines About Dogs and Marshmallows

When considering whether can dogs have marshmallows, follow these important guidelines:
1. Be Aware of the Sugar Content
Standard marshmallows contain significant amounts of sugar. A typical marshmallow consists of over 50% sugar by volume, presenting several concerns for dogs:
- Obesity and weight gain: Frequent consumption of sugary treats causes unhealthy weight gain.
- Dental issues: Sugar contributes to tooth decay and gum disease.
- Blood sugar fluctuations: Particularly problematic for dogs with diabetes or insulin sensitivities
- Digestive upset: Sugar can cause stomach discomfort, gas, or diarrhea
When evaluating are marshmallows bad for dogs, the high sugar content alone makes them a poor choice for regular treats, even if they don’t contain immediately toxic ingredients.
2. Absolutely Avoid Sugar-Free Marshmallows
This guideline is critical because it addresses a potentially life-threatening situation. When asking are marshmallows poisonous to dogs, the answer depends largely on whether they’re sugar-free.
Many sugar-free marshmallows contain xylitol, an artificial sweetener that is:
- Extremely toxic to dogs, even in small amounts
- Capable of causing rapid insulin release and hypoglycemia
- Potentially fatal if not treated immediately
- Known to cause liver failure in some cases
Always check ingredient labels carefully. If xylitol (or “sugar alcohol”) appears on the label, the product is extremely dangerous and should never be given to dogs under any circumstances.
3. Consider Choking and Obstruction Risks
The physical properties of marshmallows present hazards when determining are marshmallows safe for dogs:
- Sticky texture: Marshmallows can stick to the roof of the mouth or throat
- Expanding potential: They may expand when mixed with saliva
- Difficult to chew properly: Many dogs tend to gulp treats without adequate chewing
- Shape and size concerns: Particularly for mini marshmallows, which are small enough to be inhaled
These physical characteristics create significant choking hazards, especially for small dogs or those who eat rapidly.
4. Consider Your Dog’s Size and Health Condition
When considering whether can dogs eat marshmallows safely, it is important to take into account the specific characteristics of your individual dog.
- Small dogs: Experience more pronounced effects from even small amounts of sugar
- Dogs with diabetes: Should never consume marshmallows due to the sugar content
- Overweight dogs: Additional empty calories can exacerbate weight issues
- Dogs with dental problems: Sticky sugar compounds existing dental concerns
- Dogs with pancreatitis or a history of digestive issues: Sugar can trigger flare-ups
For most dogs with health conditions, the answer to can dogs have marshmallows should be a clear “no” regardless of the type of marshmallow.
5. Understand Marshmallows Offer No Nutritional Value
When evaluating are marshmallows bad for dogs, consider that they provide:
- Essentially zero protein
- No significant vitamins or minerals
- No fiber
- Empty calories from sugar and carbohydrates
Dogs, like humans, have limited “treat calories” they can consume without impacting their overall health. Using those calories on nutritionally empty foods means missing opportunities for healthier treat options that could actually benefit your dog.
6. Watch for Artificial Ingredients and Additives
Beyond sugar and xylitol, many marshmallows contain other ingredients that factor into whether marshmallows are safe for dogs:
- Artificial colors: May cause allergic reactions or hyperactivity in some dogs
- Artificial flavors: Can trigger digestive sensitivity
- Preservatives: May cause adverse reactions in sensitive dogs
While these ingredients aren’t typically immediately toxic like xylitol, they add to the overall problematic nature of marshmallows for canine consumption.
7. Choose Healthier Alternatives

Rather than wondering if can dogs eat marshmallows, consider offering these safer, more nutritious alternatives:
- Fresh fruits: Small pieces of apple (no seeds), blueberries, or watermelon provide natural sweetness with actual nutritional benefits
- Frozen treats: Plain yogurt (no xylitol) frozen in small dollops
- Commercial dog treats: Specifically formulated for canine nutritional needs
- Vegetables: Carrots, green beans, or cucumber slices provide crunch without sugar
- Plain popcorn: As discussed in our article about can dogs eat popcorn, plain air-popped popcorn without butter or salt can be an occasional low-calorie treat
These alternatives satisfy your dog’s desire for treats while providing actual nutritional benefits or, at minimum, doing less potential harm than sugar-laden marshmallows.
Potential Health Risks: Are Marshmallows Poisonous for Dogs?
While standard marshmallows are not directly poisonous (unlike sugar-free varieties), they do present several health risks worth considering when evaluating are marshmallows poisonous for dogs.
Short-Term Risks
Immediate concerns after marshmallow consumption may include:
- Choking: The sticky, expanding nature creates a significant choking hazard
- Digestive upset: Vomiting, diarrhea, gas, or discomfort
- Sugar rush and subsequent crash: Leading to hyperactivity followed by lethargy
- Allergic reactions: Though rare, some dogs may react to gelatin or other ingredients
Long-Term Risks of Regular Consumption
Consistently giving marshmallows to your dog can lead to:
- Obesity: With associated joint problems, reduced mobility, and shortened lifespan
- Dental disease: Including cavities, gingivitis, and eventual tooth loss
- Diabetes: Regular sugar consumption can contribute to diabetes development
- Nutritional imbalances: can occur if treats like marshmallows replace a dog’s proper food.
These long-term concerns underscore why the answer to can dogs have marshmallows should generally be “no” or at most “rarely, in very small amounts, and only regular marshmallows without chocolate or xylitol.”
Special Considerations for Specific Marshmallow Types
Different marshmallow varieties present unique concerns when determining are marshmallows safe for dogs.
Chocolate-Covered Marshmallows
Never feed chocolate-covered marshmallows to dogs. Chocolate contains theobromine and caffeine, both toxic to dogs and potentially fatal in sufficient quantities. The combination of chocolate toxicity, high sugar content, and choking risk makes these an absolute “no” when asking can dogs eat marshmallows with chocolate.
Marshmallow Fluff/Cream
While not presenting the same choking hazard as solid marshmallows, marshmallow fluff still contains:
- High sugar content
- Potentially artificial ingredients
- Zero nutritional value
The spreadable nature may make it more likely to stick to fur or furniture as well. Generally, marshmallow fluff offers the same concerns as regular marshmallows without the choking risk.
Colored or Flavored Marshmallows
Beyond the standard white variety, colored or flavored marshmallows include additional artificial ingredients that may:
- Causes digestive upset
- Contain allergens
- Include more types of sugar or sweeteners
These additional ingredients only increase concerns about whether marshmallows are bad for dogs.
Comparing Marshmallows to Other Human Sweets and Snacks
To better understand the risks of marshmallows, it’s helpful to compare them to other human foods dog owners might consider sharing.
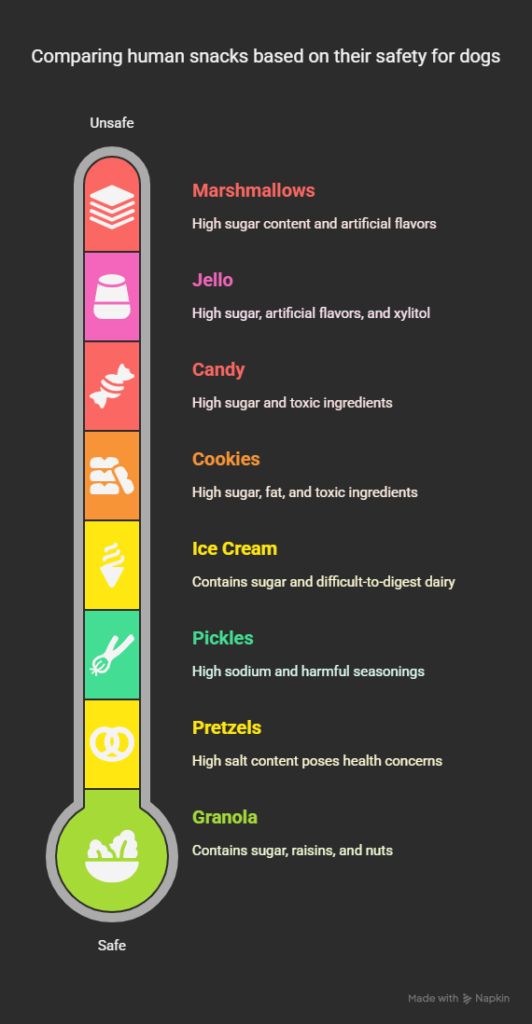
Gelatin-Based Treats
Since marshmallows contain gelatin, you might wonder about other gelatin desserts. For instance, many owners ask if dogs can eat Jello. Like marshmallows, plain gelatin itself isn’t toxic, but commercial gelatin desserts typically contain:
- High sugar content
- Artificial colors and flavors
- Potentially xylitol in sugar-free varieties
These similarities make most gelatin desserts similarly problematic for dogs.
Other Sugar-Based Treats
When comparing marshmallows to other sweet human foods:
- Candy: Most candies present the same sugar concerns as marshmallows, with additional risks from chocolate, xylitol, or other ingredients
- Cookies: Typically high in sugar and fat, with additional concerns from chocolate chips, raisins, or macadamia nuts in some varieties
- Ice cream: Contains sugar plus dairy, which many dogs have difficulty digesting
Savory Human Snacks
While exploring alternatives to sweet treats, some owners consider savory options:
- Pretzels: While not sweet, most pretzels contain significant salt, which presents its own health concerns for dogs
- Pickles: As explored in our article about can dogs eat pickles, pickles contain problematic sodium levels and potentially harmful seasonings
- Granola: Though seemingly healthier, most commercial granola contains added sugars, raisins (toxic to dogs), or nuts that can be difficult to digest
Comparing these options shows that many human snacks, whether sweet or savory, present concerns for canine consumption. This reinforces why purpose-made dog treats or simple whole foods typically represent better choices.
What To Do If Your Dog Eats Marshmallows
If you’re reading this after your dog has already consumed marshmallows, here’s what to do based on the situation:
If Your Dog Ate Regular Marshmallows:
- One or two regular marshmallows: For most medium to large dogs, monitor for digestive upset, but serious complications are unlikely
- Multiple regular marshmallows: Watch for signs of discomfort, vomiting, or diarrhea; contact your vet if symptoms develop
- Signs of choking: If your dog is coughing, gagging, or having difficulty breathing, this is an emergency requiring immediate veterinary attention
If Your Dog Ate Sugar-Free Marshmallows:
- Any amount: This is potentially an emergency situation
- Immediate action: Contact your veterinarian or an emergency animal hospital immediately
- Watch for symptoms: Vomiting, weakness, lack of coordination, seizures, or collapse
- Do not wait: Xylitol toxicity can develop rapidly and become more difficult to treat as time passes
If Your Dog Ate Chocolate Marshmallows:
- Contact your vet: Chocolate toxicity depends on the type of chocolate and amount consumed relative to your dog’s weight
- Provide information: Be ready to tell your vet what kind of chocolate marshmallows and approximately how many were consumed
- Follow professional guidance: Your vet may recommend monitoring, inducing vomiting, or bringing your dog in for treatment
Key Takeaways: Can Dogs Eat Marshmallows?
To summarize what we’ve learned about whether can dogs eat marshmallows:
- Regular marshmallows are not immediately toxic but offer no nutritional value and present several health concerns
- Sugar-free marshmallows containing xylitol are extremely dangerous and potentially fatal to dogs
- Chocolate marshmallows contain toxic compounds and should never be given to dogs
- The high sugar content in regular marshmallows can lead to obesity, dental problems, and digestive upset
- Choking hazards are significant, especially for small dogs or those who eat rapidly
- Healthier alternatives exist that can satisfy your dog’s desire for treats without the risks
- Dogs with health conditions, including diabetes, obesity, or dental problems, should avoid marshmallows entirely
Important Veterinary Disclaimer
This information is meant to teach you something, but it shouldn’t take the place of advice from a veterinarian. Before giving your dog new foods, always talk to your vet first, especially if your dog already has health problems. Call your vet right away if your dog has eaten marshmallows and is acting strangely.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Treats for Your Dog
When evaluating whether marshmallows are safe for dogs, the evidence suggests they’re best avoided or offered only in very limited circumstances. While a single plain marshmallow is unlikely to cause serious harm to a healthy adult dog, the combination of high sugar, choking risk, and lack of nutritional value makes them a poor choice for treats.
Instead, focus on providing your dog with treats specifically formulated for their nutritional needs or whole foods like fresh vegetables and limited fruit that offer actual health benefits. The best way to show love to your pet is through attention, exercise, and appropriate nutrition, not by sharing potentially problematic human foods.
For more comprehensive information about foods that are safe to share with your dog, check out our main guide on what foods can dogs eat from the table, which covers a wide range of human foods and their safety for canine consumption.
References
For more information about dog nutrition and food safety, consult these authoritative veterinary sources:
- American Kennel Club – Human Foods Dogs Can and Can’t Eat
- ASPCA Animal Poison Control Center – Toxic and Non-Toxic Plants
- PetMD
- Pet Poison Helpline – Xylitol Poisoning in Dogs
FAQs About Dogs and Marshmallows
Can puppies eat marshmallows?
Puppies should never be given marshmallows. Their developing digestive systems are more sensitive, they’re at higher risk for choking, and they need carefully balanced nutrition for proper growth. Additionally, establishing healthy treat habits early in a dog’s life sets the foundation for long-term health.
What about marshmallow root or marshmallow plant?
Marshmallow root (Althaea officinalis) is different from candy marshmallows. Some holistic veterinarians use marshmallow root preparations for certain digestive or respiratory conditions in dogs. However, this should only be done under veterinary supervision and bears no relation to giving candy marshmallows to dogs.
How many marshmallows would be toxic to a dog?
For regular marshmallows, toxicity is generally not the concern (unless they contain chocolate); rather, the issues are choking and long-term health impacts from sugar. For sugar-free marshmallows containing xylitol, as little as one small marshmallow could be dangerous for a small dog. Xylitol toxicity is weight-dependent, with as little as 50-100mg per kg of body weight potentially causing hypoglycemia.
My dog seems fine after eating a marshmallow. Is this okay?
A single incident without apparent symptoms is likely not a cause for significant concern with a regular marshmallow. However, this shouldn’t be interpreted as evidence that regular marshmallow consumption is safe. Many health effects develop gradually over time or only after repeated exposure.
Are there any commercial dog treats that are similar to marshmallows but safe?
Several companies make soft, puffy dog treats that might satisfy a dog who shows interest in marshmallows. Look for options specifically formulated for dogs, preferably with limited ingredients and without artificial colors or flavors. These provide a soft texture and treat experience without the concerns associated with human marshmallows.







